Cloud Computing – A Complete Guide to Achieve Business Objective

Cloud Computing – A Complete Guide to Achieve Business Objective

Digital transformation has become a pre-requisite for businesses, around the globe, to survive. Businesses are experiencing dire consequences of Digital Darwinism — evolve or die. To survive in today’s situation, businesses must innovate competitively. And, the cloud emerges as the fuel to digital transformation.
Nowadays, CIOs, CEOs, and CTOs are on the front foot to adapt to digital transformation with cloud computing strategy. The cloud computing services market has become a $200 billion industry that is experiencing phenomenal growth in recent years and is expected to continue. Gartner says the growth of the cloud will reach up to 17% this year as cloud services are important to many business operations around the globe. The US is the most considerable public cloud market.
Due to modern technology and an increase in the cloud industry, many businesses expect to increase their cloud budget by almost 50%. But they still struggle to leverage the technology because some core concepts need clarification.
What is cloud computing? Who introduced the cloud? What are the benefits? We will be discussing all this in this blog. To start with –
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is an interconnected system of Internet-hosted distant servers to manage, store, and process data. It is the on-demand availability of computer services, using digital technology trends, over the Internet to offer business innovation, agility, and growth.
The main motivation behind cloud computing is to enable businesses to get access to data centers and manage tasks from a remote location. Cloud computing works on the pay-as-you-go pricing model, which helps businesses lower their operating cost and run infrastructure more efficiently.
The History of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing appears to us as a new idea but is not so new. The cloud was introduced in the early 1950s. In the year 1955, John McCarthy developed a time-sharing concept that enables users to use expensive mainframe simultaneously.
The idea to enable users was through sharing a virtual computing experience that came out in the year 1963. This offered a path to MIT’s advancement of the first virtual machine, also called the computer.
Around the 1960s, the idea of cloud computing went big, when an American computer scientist Joseph Carl Robnett Licklider depicted a hypothesis of interconnected computing systems on ARPANET. Licklider’s commitment is considered as the most significant in the production of cloud computation, therefore, accepted to be the father of cloud computing.
Types of Cloud Computing
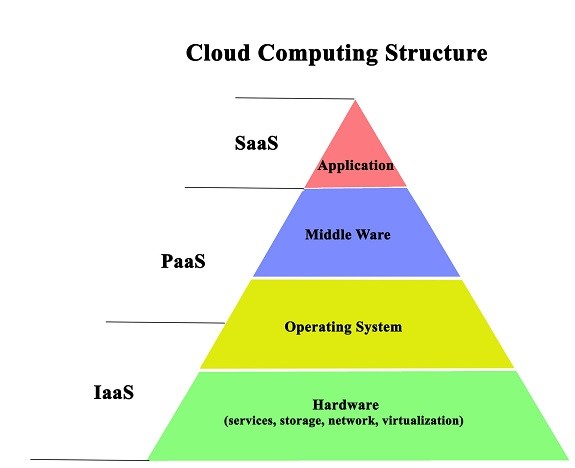
The 3 types of popular cloud services include Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Cloud computing services give the chance to businesses to embrace the best-suited service delivery models to address business needs with ability and agility. Consequently, it’s crucial to know the difference between each service to choose “the one” that suits your business requirements better and make your cloud experience smooth and advantageous.
IaaS
IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service) gives a significant or raw computing service which requires a higher level of IT skill. Thus, it is generally perfect for IT administrators who want to control servers in the cloud instead of visiting physical locations. This service gives a cloud server, as well as data storage space to access computing power but without installation and maintenance trouble.
IaaS Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Compute Engine, and Microsoft Azure
PaaS
“58% of those enterprises that have invested in PaaS expect a positive ROI in less than three months.”
PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service) provides a robust framework for application developers to develop, test, and manage new customized applications. It is ideal for software developers to deploy applications, from simple to complex, without the need for any infrastructure like databases, servers, operating systems, development tools, etc.

PaaS helps businesses to manage their applications and programming all alone by using several software development technologies, such as .Net, Python, and Java.
PaaS Examples: Google App Engine, Heroku, and OpenShift
SaaS
“73% of businesses state that almost all of their applications will be SaaS-powered by this year.”
Saas (Software-as-a-Service) is the cloud’s biggest and most developed service that provides programming or a set of applications available in the cloud. SaaS cloud service is designed for end-users which is designed and delivered over the internet.
SaaS empowers users to download, store, and access data to the cloud drive via the internet, which helps save computer memory. This helps users to forego the traditional course of downloading and then storing the heavy software on their hard drive.
SaaS Examples: Dropbox, Office 365, Google Doc, and CRM software
The Top Benefits of Cloud Computing
Here are the common yet most important benefits that leaders need to know while stimulating their journey towards the cloud effectively.
Save Capital Expenditure
Businesses can now save big bucks on IT services like maintenance and storage of the data. There is no need to manage any in-house infrastructure equipment and spend money to update hardware or buy software licenses. The Cloud services enable companies to expand easily in the future with on-demand resources which saves time and lowers costs.
Flexibility and Mobility
Cloud computing enables users to scale/descale infrastructure on-demand with ease, which results in the ideal use of resources. Cloud consulting services allow users to assess the resources remotely anytime & anywhere through smartphones, tablets, laptops, and so on. Therefore, flexibility and mobility are essential benefits that make employees productive.
Upgraded IT Security
IT security plays a crucial role in online businesses. Many businesses compromise their data due to security breaches or assaults. Cloud computing makes servers and storage secure by defining the security levels and implementing continuous detection systems. The more the cloud computing models are developing, the more the users are relieved from the fear of losing data.
Competitive Edge
Companies that are using cloud computing services develop a competitive edge for the competitors as compared to those who don’t. Since the cloud helps businesses to access the latest technology or application anytime and anywhere, they won’t feel obsolete in this fast-growing world. It enables the company to focus on collaboration, production, security, and revenue without wasting time in installing and managing business applications.
Ensures Business Continuity
Business operations can be influenced and may disrupt for a long period in situations like technology interruption, equipment failure, or even unexpected fiascos like fire or flood. Cloud computing provides continuous IT services to ensure advanced business operations during such emergencies. The remote working abilities offered by cloud models ensure that the user’s data is stored securely and can be accessed remotely whenever needed. Clouds ensure continuous integration of data leveraging the advanced technology and tools to promote business.
The Verdict: Cloud Computing is the New Normal
Cloud computing continues to evolve year over year and is now considered the new normal. The future of cloud computing is quickly entering the ‘phygital’ world. It empowers businesses to use inventive approaches to improve and succeed in their business objectives. Embracing the cloud allows businesses to run efficiently, serve customers better, and boost their revenue to stay ahead of the competitors.
